(last updated 2023)
Drinking Water & Health in Rural Appalachia
Start Year: 2020 | End Year: Ongoing
 We are working on a number of projects to better understand issues related to drinking water (access, quality, use), sanitation, and reported and measured health outcomes in the Appalachia region, with a focus on children and adults living in Central Appalachia. In 2020, we started a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis study to identify and synthesize published research on drinking water contamination and associated health outcomes in the Appalachian region over a 20-year time period. We pre-registered our study protocols, completed data extraction and analysis in 2022, and published our findings in 2023 – the limited number and nature of the studies identified demonstrated that more epidemiologic research is needed to understand exposures to drinking water contaminants in this region. From 2021 to 2023, in collaboration with UVA, ETSU, a regional non-profit, a local utility, and others, we conducted a water-and-health focused cross-sectional study and a prospective cohort study in southwest VA (an important component of these studies is that we also share water testing results with participating households). In 2022, we published findings from the cross-sectional study (a small community of households with private wells), and we anticipate publishing preliminary findings from the cohort study (rural households with utility-supplied and private well and spring water in two counties) in early 2024. Given the relatively high rates of bottled water use/reliance we observed in rural households, we also conducted a study to analyze the quality of bottled water sold in the region; we anticipate publishing those findings in 2024. Building on findings from these studies, in late 2023 (in collaboration with ETSU, a regional non-profit, and others) we initiated a prospective safe water intervention pilot study in rural regions of southwest VA and northeast TN.
We are working on a number of projects to better understand issues related to drinking water (access, quality, use), sanitation, and reported and measured health outcomes in the Appalachia region, with a focus on children and adults living in Central Appalachia. In 2020, we started a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis study to identify and synthesize published research on drinking water contamination and associated health outcomes in the Appalachian region over a 20-year time period. We pre-registered our study protocols, completed data extraction and analysis in 2022, and published our findings in 2023 – the limited number and nature of the studies identified demonstrated that more epidemiologic research is needed to understand exposures to drinking water contaminants in this region. From 2021 to 2023, in collaboration with UVA, ETSU, a regional non-profit, a local utility, and others, we conducted a water-and-health focused cross-sectional study and a prospective cohort study in southwest VA (an important component of these studies is that we also share water testing results with participating households). In 2022, we published findings from the cross-sectional study (a small community of households with private wells), and we anticipate publishing preliminary findings from the cohort study (rural households with utility-supplied and private well and spring water in two counties) in early 2024. Given the relatively high rates of bottled water use/reliance we observed in rural households, we also conducted a study to analyze the quality of bottled water sold in the region; we anticipate publishing those findings in 2024. Building on findings from these studies, in late 2023 (in collaboration with ETSU, a regional non-profit, and others) we initiated a prospective safe water intervention pilot study in rural regions of southwest VA and northeast TN.
Funding & Support




Poverty, Water, Climate Change, & Health in Sub-Saharan Africa
Start Year: 2020 | End Year: Ongoing

As described below (see other project summaries), the Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool (MPAT) was created in two phases (from 2008 to 2014) via a collaborative, international initiative to develop, test, and pilot a new tool for local-level rural poverty assessment. The work was guided by a Sounding Board of experts from the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), other United Nations agencies, international and regional organizations, and universities around the world (see www.ifad.org/mpat). Following MPAT’s finalization and institutionalization in 2014, it was used in multiple countries including many in Sub-Saharan Africa. We are currently working on multiple desk-based studies with a variety of collaborators to analyze data from ~7,000 households across Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Mali, Tanzania, and Zimbabwe. Because MPAT was developed based primarily on data from Bangladesh, China, India, and Mozambique, one study we are leading is an updated assessment and evaluation of MPAT’s indicator structure and robustness based on its use in the sub-Saharan region. Other studies we are working on focus on a cross-county analyses of MPAT’s water, climate change, and health focused components and sub-components, and related programs and interventions. We anticipate publishing a number of papers on this research in 2024.
Funding & Support



Wastewater Surveillance & Epidemiology at Multiple Scales
Start Year: 2020 | End Year: Ongoing
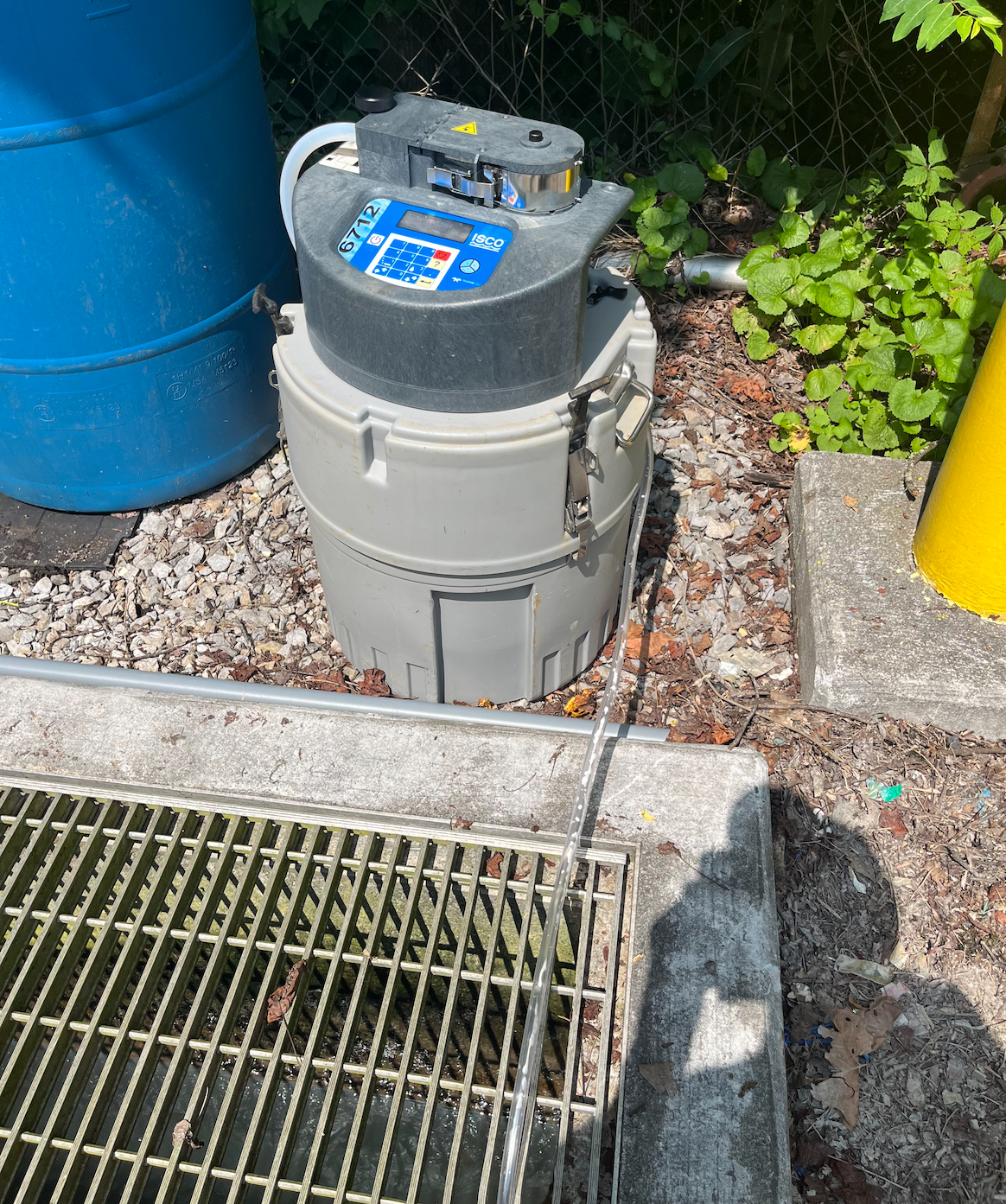

As of 2022, our research efforts have primarily focused on wastewater-based surveillance (WBS) and epidemiology in rural settings, with the overarching goal of developing improved methods and guidelines for the implementation of responsible, reliable, and ethical WBS for rural communities. The foundation of this effort was established during the 2020/21 academic year, when Dr.s Pruden & Vikesland in Environmental Engineering led an initiative with collaborators across Virginia Tech (and at HRSD) to collect and analyze wastewater samples from different buildings and sites across the university campus with the goal of developing a coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) surveillance program. WBS has been used by many other research groups, as well as wastewater utilities, to monitor SARS-CoV-2 (i.e., the virus that causes COVID-19) trends. Our primary research objective for that study was to evaluate the use of WBS and epidemiologic methods to monitor and predict SARS-CoV-2 virus trends at sub-sewershed scales. Using pre-specified analyses, we showed that the detection of SARS-CoV-2 genes in wastewater samples was associated with statistically significant increases in COVID-19 cases 8 days after sample collection. We published our methods and findings from this research in 2022. In the summer of 2022, our research group – in collaboration with VT faculty members Pruden, Vikesland, Krometis, students in their groups, and Dr. Taniuchi’s group at UVA – initiated a WBS research study in partnership with a utility in southwest Virginia. We started a monthly sub-sewershed sampling campaign in September 2022 (photo is of a composite sampler at the wastewater treatment plant), which was completed in August 2023. We anticipate publishing initial findings from this research in 2024, and are currently working to build and expand on these efforts at other sites in 2024 and 2025, in collaboration with the Virginia Department of Health and others.
Funding & Support





Arsenic in Rural & Carceral Drinking Water Systems
Start Year: 2018 | End Year: 2021
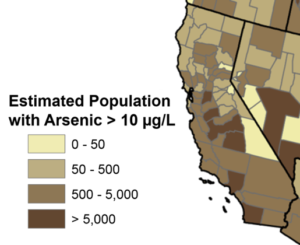
Source: Adapted from www.USGS.gov
In the United States, millions of people lack reliable access to safe drinking water, a problem that is particularly acute in low-income rural areas. California legally recognized the human right to water in 2012, but this right remains unevenly realized. To better understand the status of the human right to water in rural communities, we analyzed 20 years of publicly available drinking water quality monitoring and violation data from 2001-2021, with a focus on arsenic contamination (a carcinogenic heavy metal) from a state prison as well as public water systems in three neighboring rural communities in southern California. We found that all four of these drinking water systems repeatedly exceeded the legal limit for arsenic during the study period, with mean served arsenic levels ranging from 3.4 (SD=6.7) to 9.3 (SD:=2.9) μg/L across the systems (based on 2,426 samples from four systems). In addition to arsenic-specific findings and comparisons across these four sites, our analyses demonstrate how publicly reported annually averaged water quality data (used to monitor system violations and to track progress toward the human right to water) provide only a partial guide to whether the right to safe water is being realized. We published our findings in 2022.
Funding & Support


![]()
Wastewater & Coastal Environmental Health in the Philippines
Start Year: 2018 | End Year: 2022
 This research collaboration between colleagues at the University of California Berkeley (UCB) and the University of the Philippines (UPD) was designed to advance methods for measuring, modelling, and assessing marine water quality and environmental health at three sites in the Philippines. One of the three study sites for this multi-year project is Boracay Island. A popular tourist destination, in recent years sewage and other contaminants have adversely impacted Boracay’s beaches and coastal water quality, with implications for both environmental and human health. This research project centers on the use of an autonomous surface vessel to collect a wide range of spatially referenced data which can be combined with data from water samples and lab-based analyses, as well as satellite and other remote sensed data. At the Boracay site, proxy sensor data (e.g., optical brighteners and tryptophan) and laboratory analyses of grab samples will be combined to map and model actual and estimated water quality and environmental health impacts from point and non-point runoff and wastewater effluent. Our planned research activities and associated timelines suffered from a variety of logistical setbacks and delays, as well as delays related to the COVID-19 Pandemic. We anticipate publishing findings from this work starting in 2023.
This research collaboration between colleagues at the University of California Berkeley (UCB) and the University of the Philippines (UPD) was designed to advance methods for measuring, modelling, and assessing marine water quality and environmental health at three sites in the Philippines. One of the three study sites for this multi-year project is Boracay Island. A popular tourist destination, in recent years sewage and other contaminants have adversely impacted Boracay’s beaches and coastal water quality, with implications for both environmental and human health. This research project centers on the use of an autonomous surface vessel to collect a wide range of spatially referenced data which can be combined with data from water samples and lab-based analyses, as well as satellite and other remote sensed data. At the Boracay site, proxy sensor data (e.g., optical brighteners and tryptophan) and laboratory analyses of grab samples will be combined to map and model actual and estimated water quality and environmental health impacts from point and non-point runoff and wastewater effluent. Our planned research activities and associated timelines suffered from a variety of logistical setbacks and delays, as well as delays related to the COVID-19 Pandemic. We anticipate publishing findings from this work starting in 2023.
Funding & Support

Electric Kettle Promotion Program in Rural China (RCT)
Start Year: 2017 | End Year: 2022
 Results from our previous research in rural China suggests that increasing the use of electric kettles for boiling (i.e., treating) drinking water in low-income areas of rural China could help expand access to safer drinking water, reduce household air pollution, and improve environmental and health outcomes in rural Chinese households currently boiling drinking water with solid-fuels (or not treating their water, or drinking contaminated bottled water). Our study was designed (and pre-registered on Chinese Clinical Trials Register & ClinicalTrials.gov) to evaluate the impact of a pilot Rural Electric Kettle Promotion Program offered to low-income households in rural Anhui Province, China. Specifically, we used a parallel arm cohort cluster-randomized controlled (RCT) trial design with a 1:1 ratio to randomize 30 villages (i.e., clusters) to treatment or control using stratified randomization by geography and by cluster proportions of reported electric kettle use at baseline (900 households total).
Results from our previous research in rural China suggests that increasing the use of electric kettles for boiling (i.e., treating) drinking water in low-income areas of rural China could help expand access to safer drinking water, reduce household air pollution, and improve environmental and health outcomes in rural Chinese households currently boiling drinking water with solid-fuels (or not treating their water, or drinking contaminated bottled water). Our study was designed (and pre-registered on Chinese Clinical Trials Register & ClinicalTrials.gov) to evaluate the impact of a pilot Rural Electric Kettle Promotion Program offered to low-income households in rural Anhui Province, China. Specifically, we used a parallel arm cohort cluster-randomized controlled (RCT) trial design with a 1:1 ratio to randomize 30 villages (i.e., clusters) to treatment or control using stratified randomization by geography and by cluster proportions of reported electric kettle use at baseline (900 households total).
[Notes: We pre-specified and pre-registered our statistical analysis plan, but data cleaning and analysis were significantly delayed due to the COVID19 pandemic; we anticipate publishing primary findings starting in 2026]
Funding & Support



Water Utilities & Intermittent Drinking Water Supply in China
Start Year: 2017 | End Year: 2019
 Led by our colleague, Dr. Hongxing Li at the China CDC, this project focused on the management and use of drinking water supply in areas where utilities provide piped drinking water, but for a variety of reasons it is not provided continuously (i.e., piped connections are not supplied with treated drinking water 24 hours a day, 7 days a week). This situation – that of intermittent water supply (IWS) – is relatively widespread in many low- and middle-income countries, as well as in parts of China. This research project, conducted in two Chinese provinces (Shandong and Hubei), assessed and compared management and consumer adaptation strategies, as well as drinking water quality, storage practices, and behaviors and beliefs associated with IWS, with comparison to similar communities living under conditions of continuous water supply (CWS). Water samples (from taps and rooftop storage units) and survey data were collected from 400 households across four villages (2 IWS, 2 CWS) in the two provinces. One of the main reasons the utilities in these regions provided water intermittently was to reduce the electricity costs associated with water supply pumps. Indicators of microbiological contamination were higher in samples from the IWS villages compared with the CWS villages, and we observed higher rates of bottled water use in the IWS villages compared with the CWS villages. As a result of this work, we were able to offer evidence-based recommendations utilities could adopt to reduce water-and-health related risks associated with IWS or transition to CWS.
Led by our colleague, Dr. Hongxing Li at the China CDC, this project focused on the management and use of drinking water supply in areas where utilities provide piped drinking water, but for a variety of reasons it is not provided continuously (i.e., piped connections are not supplied with treated drinking water 24 hours a day, 7 days a week). This situation – that of intermittent water supply (IWS) – is relatively widespread in many low- and middle-income countries, as well as in parts of China. This research project, conducted in two Chinese provinces (Shandong and Hubei), assessed and compared management and consumer adaptation strategies, as well as drinking water quality, storage practices, and behaviors and beliefs associated with IWS, with comparison to similar communities living under conditions of continuous water supply (CWS). Water samples (from taps and rooftop storage units) and survey data were collected from 400 households across four villages (2 IWS, 2 CWS) in the two provinces. One of the main reasons the utilities in these regions provided water intermittently was to reduce the electricity costs associated with water supply pumps. Indicators of microbiological contamination were higher in samples from the IWS villages compared with the CWS villages, and we observed higher rates of bottled water use in the IWS villages compared with the CWS villages. As a result of this work, we were able to offer evidence-based recommendations utilities could adopt to reduce water-and-health related risks associated with IWS or transition to CWS.
Funding & Support


Bottled Water Safety & Use in Low- & Middle-Income Countries
Start Year: 2016 | End Year: 2021
 In the course of our work studying drinking water access, contamination, and treatment in rural areas, we have observed relatively high rates of bottled water use. The reasons for increasing bottled water use in rural areas of low- and middle-income countries are varied, but available data indicates that some of the primary reasons are related to perceptions that bottled water is convenient and safer than available drinking water sources. Results from some of our research studies suggest, however, that bottled water may not always be safe. To better understand increasing use of and reliance on bottled water in LMICs we studied available market data which shows that more than half of the top-ten bottled water consuming countries globally are LMICs, and that bottled water use in LMICs is growing rapidly. With respect to global environmental health this trend is problematic in a number of respects, and, we argue, this increasing reliance on bottled water will likely hamper efforts to provide safe and affordable drinking water for all – one of the key objectives of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. As part of this work, we wish to better understand the nature and extent of bottled water contamination; however, there is relatively little publicly available data on bottled water quality, in LMICs or in high-income countries. To complement one of the only systematic review studies examining bottled water use and safety in LMICs, we conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of publicly available research studies on bottled water quality and associated health outcomes in China. After reviewing 7,000+ Chinese-language records, we extracted and analyzed data from 200+ eligible articles; we published our findings from this research in early 2022.
In the course of our work studying drinking water access, contamination, and treatment in rural areas, we have observed relatively high rates of bottled water use. The reasons for increasing bottled water use in rural areas of low- and middle-income countries are varied, but available data indicates that some of the primary reasons are related to perceptions that bottled water is convenient and safer than available drinking water sources. Results from some of our research studies suggest, however, that bottled water may not always be safe. To better understand increasing use of and reliance on bottled water in LMICs we studied available market data which shows that more than half of the top-ten bottled water consuming countries globally are LMICs, and that bottled water use in LMICs is growing rapidly. With respect to global environmental health this trend is problematic in a number of respects, and, we argue, this increasing reliance on bottled water will likely hamper efforts to provide safe and affordable drinking water for all – one of the key objectives of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. As part of this work, we wish to better understand the nature and extent of bottled water contamination; however, there is relatively little publicly available data on bottled water quality, in LMICs or in high-income countries. To complement one of the only systematic review studies examining bottled water use and safety in LMICs, we conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of publicly available research studies on bottled water quality and associated health outcomes in China. After reviewing 7,000+ Chinese-language records, we extracted and analyzed data from 200+ eligible articles; we published our findings from this research in early 2022.
Funding & Support


Evaluating Household-level Drinking Water Treatment in Rural China
Start Year: 2012 | End Year: 2014
 After extensive discussion and planning, we started a collaborative research project with colleagues at the NCRWSTG and China CDC to characterize and assess methods of household water treatment (HWT) in low-income regions of rural China. During the first phase of this research, in the summer of 2013, we collected drinking water samples and administered surveys to 450 households across 15 rural villages in Guangxi province. To assess seasonal factors, we undertook a second round of data collection in the winter of 2013/2014 during which time we also affixed remote temperature sensors to kettles and pots to help corroborate reported boiling data. In 2014, under the supervision of China CDC colleagues Director Tao Yong and Dr. Qing Luo, we replicated the study in Henan province, collecting data from 450+ rural households during the summer. Using a variety of modeling approaches, we evaluated the microbiological effectiveness of the HWT methods used – including bottled water (large 19L bottles) – and isolated socioeconomic predictors associated with HWT and water-related beliefs and behaviors. Among other findings, we observed that indicators of fecal contamination were lowest in drinking water samples from households using electric kettles. Our analyses of boiling-associated air pollution indicated that switching from boiling with pots and solid fuels to boiling with electric kettles would result in a measurable reduction in indoor air pollution. We also observed relatively high rates of microbiological contamination in samples from households using bottled water; and our analyses of socioeconomic factors suggested that rural bottled water use will continue to increase in the future. Results from these studies – as well as a systematic review on boiling and health outcomes – were also used to support and inform the design of an intervention to promote the use of electric kettles in low-income rural communities (see project summary above).
After extensive discussion and planning, we started a collaborative research project with colleagues at the NCRWSTG and China CDC to characterize and assess methods of household water treatment (HWT) in low-income regions of rural China. During the first phase of this research, in the summer of 2013, we collected drinking water samples and administered surveys to 450 households across 15 rural villages in Guangxi province. To assess seasonal factors, we undertook a second round of data collection in the winter of 2013/2014 during which time we also affixed remote temperature sensors to kettles and pots to help corroborate reported boiling data. In 2014, under the supervision of China CDC colleagues Director Tao Yong and Dr. Qing Luo, we replicated the study in Henan province, collecting data from 450+ rural households during the summer. Using a variety of modeling approaches, we evaluated the microbiological effectiveness of the HWT methods used – including bottled water (large 19L bottles) – and isolated socioeconomic predictors associated with HWT and water-related beliefs and behaviors. Among other findings, we observed that indicators of fecal contamination were lowest in drinking water samples from households using electric kettles. Our analyses of boiling-associated air pollution indicated that switching from boiling with pots and solid fuels to boiling with electric kettles would result in a measurable reduction in indoor air pollution. We also observed relatively high rates of microbiological contamination in samples from households using bottled water; and our analyses of socioeconomic factors suggested that rural bottled water use will continue to increase in the future. Results from these studies – as well as a systematic review on boiling and health outcomes – were also used to support and inform the design of an intervention to promote the use of electric kettles in low-income rural communities (see project summary above).
Funding & Support




Refinement & Finalization of the Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool (MPAT)
Start Year: 2010 | End Year: 2014
 Following the release of the working-paper User’s Guide for the Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool (MPAT) in 2009, a number of agencies and universities used the beta-version of MPAT in a variety of settings. In order to finalize MPAT and develop a comprehensive User’s Guide and associated resources, we built on the lessons learned from early adopters of the the tool (e.g., an NGO in Kenya) and iteratively used and evaluated the tool with IFAD-supported projects in Bangladesh and Mozambique. Details on the participatory expert elicitation methods we used are provided in a Journal of Development Studies paper. We developed an Excel-based data entry platform so users could easily calculate MPAT’s indicators at household, village, and project levels. We also wrote a comprehensive, 300+ page, 2014 MPAT User’s Guide which provides step-by-step instructions for using MPAT as well as training modules and materials, all with the goal of making MPAT an accessible open-source tool. The User’s Guide and accompanying resources were presented at a 2014 launch event in Rome. Since its 2014 release, MPAT has been translated into a number of languages, an optional 11th component focused on climate change was added, and MPAT has been used by a variety of agencies and institutions around the world. MPAT publications and related resources are available at www.ifad.org/mpat.
Following the release of the working-paper User’s Guide for the Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool (MPAT) in 2009, a number of agencies and universities used the beta-version of MPAT in a variety of settings. In order to finalize MPAT and develop a comprehensive User’s Guide and associated resources, we built on the lessons learned from early adopters of the the tool (e.g., an NGO in Kenya) and iteratively used and evaluated the tool with IFAD-supported projects in Bangladesh and Mozambique. Details on the participatory expert elicitation methods we used are provided in a Journal of Development Studies paper. We developed an Excel-based data entry platform so users could easily calculate MPAT’s indicators at household, village, and project levels. We also wrote a comprehensive, 300+ page, 2014 MPAT User’s Guide which provides step-by-step instructions for using MPAT as well as training modules and materials, all with the goal of making MPAT an accessible open-source tool. The User’s Guide and accompanying resources were presented at a 2014 launch event in Rome. Since its 2014 release, MPAT has been translated into a number of languages, an optional 11th component focused on climate change was added, and MPAT has been used by a variety of agencies and institutions around the world. MPAT publications and related resources are available at www.ifad.org/mpat.
Funding & Support


Developing a Thematic Indicator for Rural Poverty Assessment (MPAT)
Start Year: 2008 | End Year: 2009
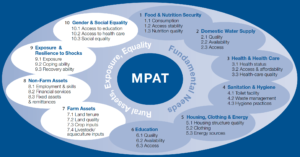 The Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Project was a collaborative, international initiative to develop, test, and pilot a new tool for local-level rural poverty assessment. The work was supported by IFAD and guided by a Sounding Board of experts from IFAD, other United Nations agencies, international and regional organizations, and universities around the world, with the majority of its members coming from the Asia region where we developed and tested the tool in China and India. Surveys (household and village level) were developed and tested in an iterative and participatory fashion, as was the indicator structure used to aggregate sub-components and components. The resulting Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool (MPAT) provides an assessment, an overview, of ten dimensions central to rural livelihoods, highlighting where additional support or interventions are likely to be most needed. The tool was designed to be universal enough to be relevant to most rural contexts around the world, yet specific enough to provide project managers and others a detailed overview of key dimensions relevant to rural poverty reduction efforts. MPAT was independently evaluated by the European Commission Joint Research Center and a working-paper version of MPAT User’s Guide was released in 2009 as well as the 2009 MPAT Book, which provides a detailed description of why and how the tool was developed. MPAT’s theoretical foundations are described in a 2010 article in Development and Practice.
The Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Project was a collaborative, international initiative to develop, test, and pilot a new tool for local-level rural poverty assessment. The work was supported by IFAD and guided by a Sounding Board of experts from IFAD, other United Nations agencies, international and regional organizations, and universities around the world, with the majority of its members coming from the Asia region where we developed and tested the tool in China and India. Surveys (household and village level) were developed and tested in an iterative and participatory fashion, as was the indicator structure used to aggregate sub-components and components. The resulting Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool (MPAT) provides an assessment, an overview, of ten dimensions central to rural livelihoods, highlighting where additional support or interventions are likely to be most needed. The tool was designed to be universal enough to be relevant to most rural contexts around the world, yet specific enough to provide project managers and others a detailed overview of key dimensions relevant to rural poverty reduction efforts. MPAT was independently evaluated by the European Commission Joint Research Center and a working-paper version of MPAT User’s Guide was released in 2009 as well as the 2009 MPAT Book, which provides a detailed description of why and how the tool was developed. MPAT’s theoretical foundations are described in a 2010 article in Development and Practice.
Funding & Support



