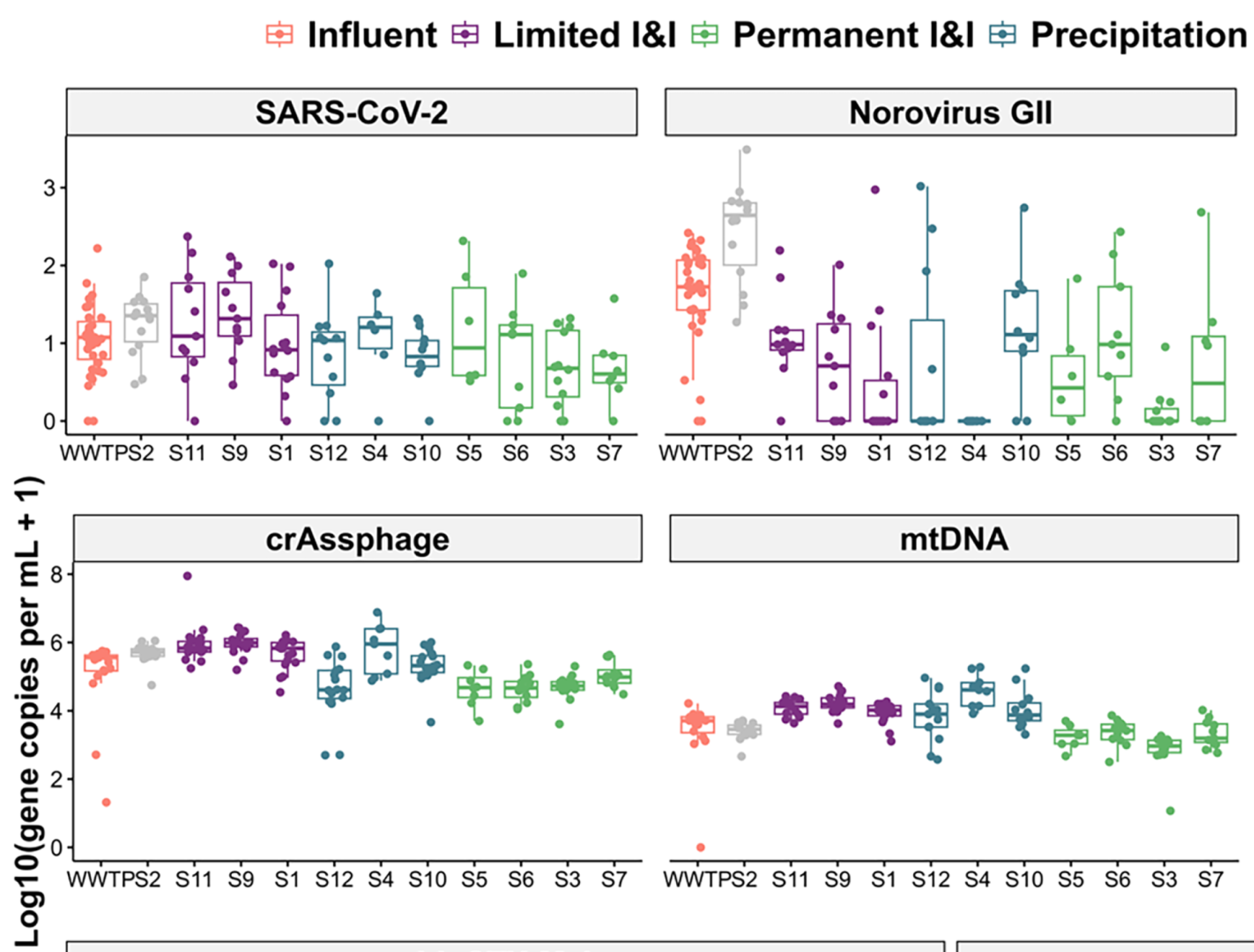
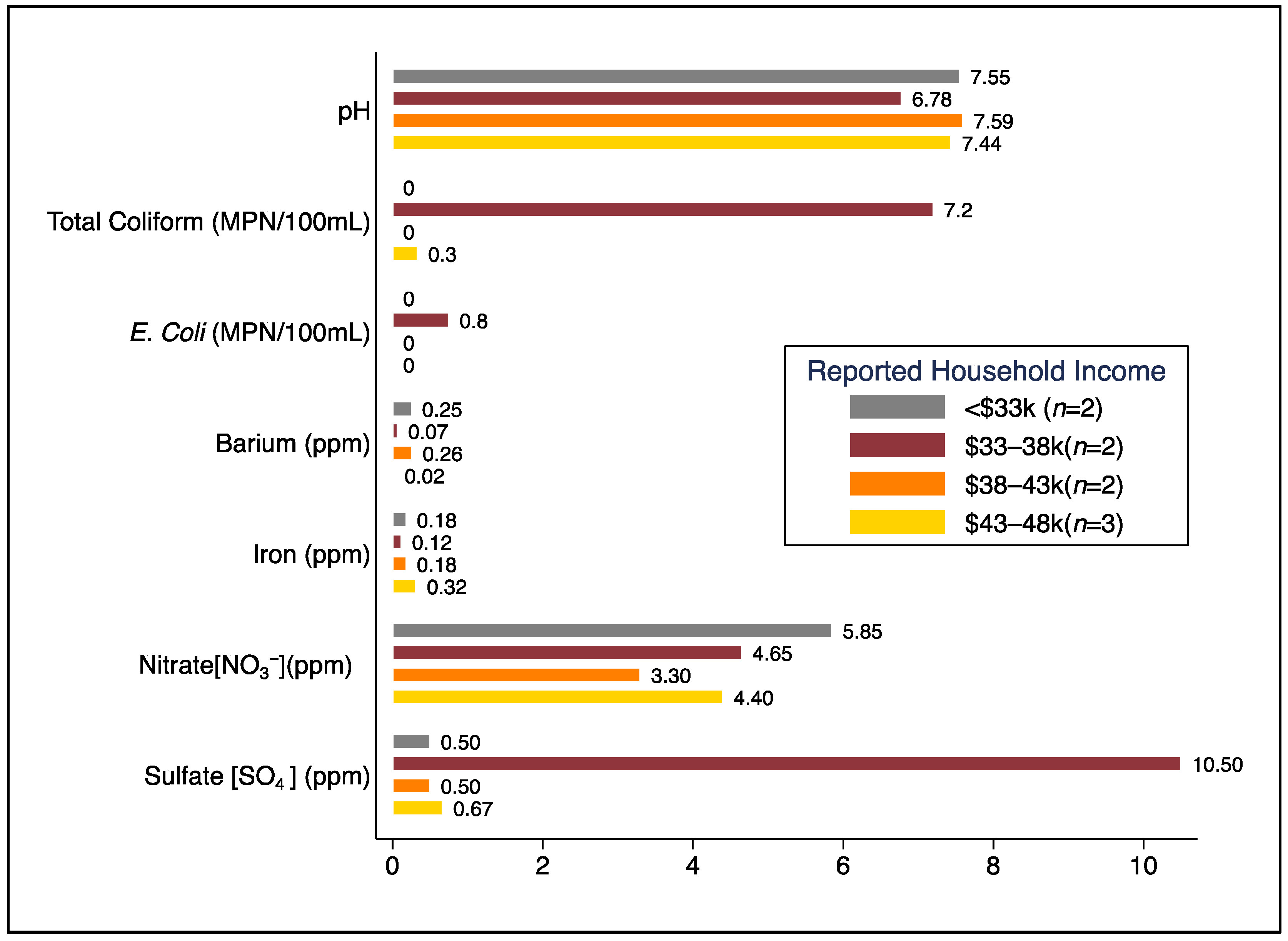Subsewershed analyses of the impacts of inflow and infiltration on viral pathogens and antibiotic resistance markers across a rural sewer system
Authors: Darling, A., Davis, B., Byrne, T., Deck, M., Rivera, G., Price, S., Amaral-Torres, A., Markham, C., Gonzalez, R., Vikesland, P., Krometis, L.-A., Pruden, A., & Cohen, A.*
Publication Year: 2025 | Journal / Publisher: Water Research
Abstract/Summary: As wastewater-based surveillance (WBS) is increasingly used to track community-level disease trends, it is important to understand how pathogen signals can be altered by phenomena that occur within sewersheds such as inflow and infiltration (I&I). Our objectives were to characterize I&I across a rural sewershed and assess potential impacts on viral (rotavirus, norovirus GII, and SARS-CoV-2), fecal indicator (HF183, the hCYTB484 gene specific to the human mitochondrial genome, and crAssphage), and antimicrobial resistance (intI1, blaCTX−M-1) targets. In a small town in Virginia (USA), we collected 107 wastewater samples at monthly intervals over a 12-month period (2022–2023) at the wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) influent and 11 up-sewer sites. Viral, fecal indicator, and antimicrobial resistance targets were enumerated using ddPCR. We observed the highest concentrations of human fecal markers and a measure anthropogenic pollution and antibiotic resistance (intI1) in up-sewer sites with limited I&I. However, median viral gene copy concentrations were highest at the WWTP, compared to 100 % (n = 11), 90 % (n = 10), and 55 % (n = 6) of up-sewer sites for rotavirus, norovirus GII, and SARS-CoV-2, respectively. After adjusting for covariates (Ba, COD, dissolved oxygen, groundwater depth, precipitation, sampling date) using generalized linear models, moderate to high I&I was associated with statistically significant reductions in log10-transformed rotavirus and norovirus GII concentrations across the sewershed (coefficients = -0.7 and -0.9, p < 0.001, n = 95), though not for SARS-CoV-2 (coefficient = -0.2, p = 0.181, n = 95). Overall, we found that while I&I can diminish biomarker signals throughout a sewershed, including at the WWTP influent, I&I impacts vary depending on the target, and pathogen biomarker signals were, on average, higher and less variable over time at the WWTP compared to most up-sewer sites. As far as we are aware, this is the first study to assess in situ I&I impacts on multiple WBS targets. Taken together, our findings highlight challenges and tradeoffs associated with different sampling strategies for different WBS targets in heavily I&I impacted systems.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
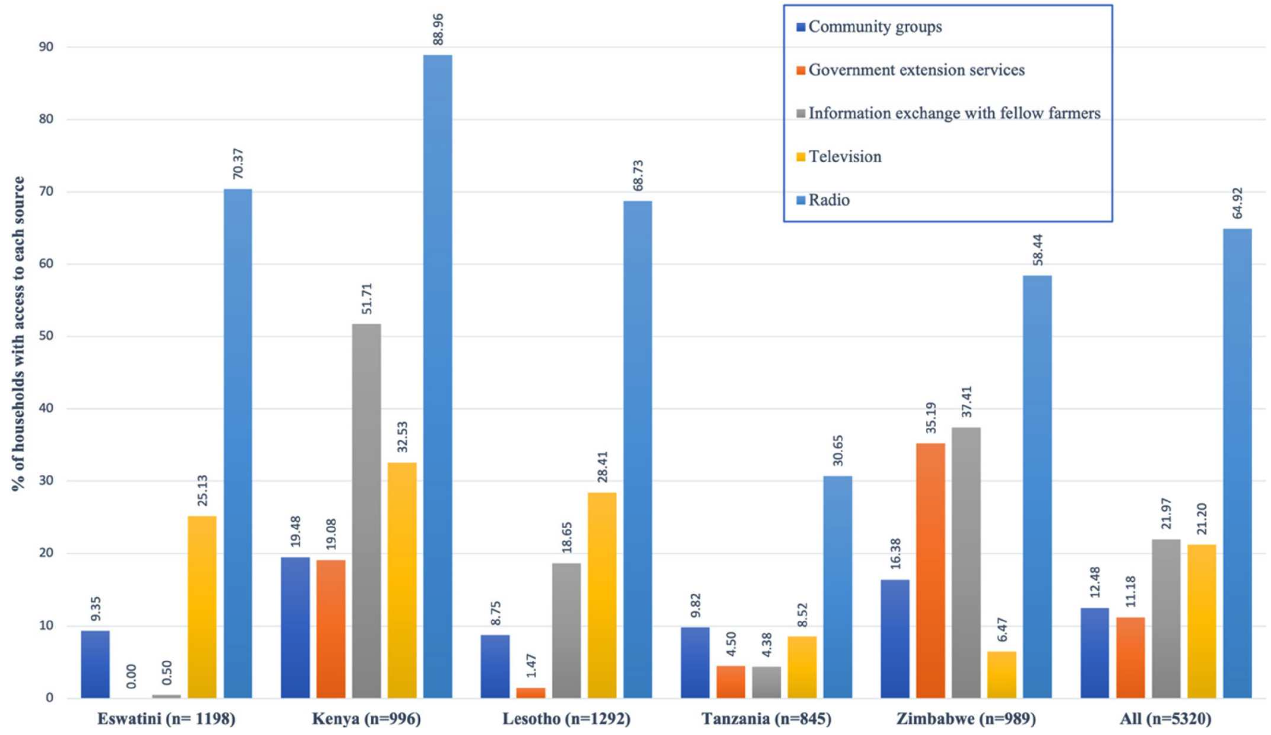
Climate information access and use in East and Southern Africa: identifying linkages between smallholder household characteristics and climate change adaptation
Authors: Minjauw, F. Rasheduzzaman, M., Huang, J., Lozano, A., Baumgartner, P., Doward, P., Clarkson, G., & Cohen, A.*
Publication Year: 2024 | Journal / Publisher: Climate and Development
Abstract/Summary: Climate change adversely impacts the livelihoods of smallholder farmers across East and Southern Africa. Climate-related information is assumed to support smallholder farmer decision-making and use of adaptive practices as a means to improve livelihoods, resiliency and levels of food security. However, the value of climate information provision and its role in promoting adaptive practices remains poorly understood. We examined smallholder household access to, and use of, climate information. Survey data was collected from 5322 households across Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Tanzania and Zimbabwe using the Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool. Overall, the majority of households regularly accessed at least one source of climate information, primarily via radio (64.9%, n = 3453). Our statistical models showed that households with relatively better access to credit and land tenure were more likely to receive climate information (p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively, n = 1421), and of those, households who reported observing past climate-related changes were more likely to actually use climate information (p < 0.05, n = 1097). Secure land tenure was positively associated with information use, though not statistically significant. Findings from our study offer guidance for improving the targeting and delivery of climate information programmes and policies, and indicate that the assumed benefits of climate information provision should be more rigorously evaluated.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
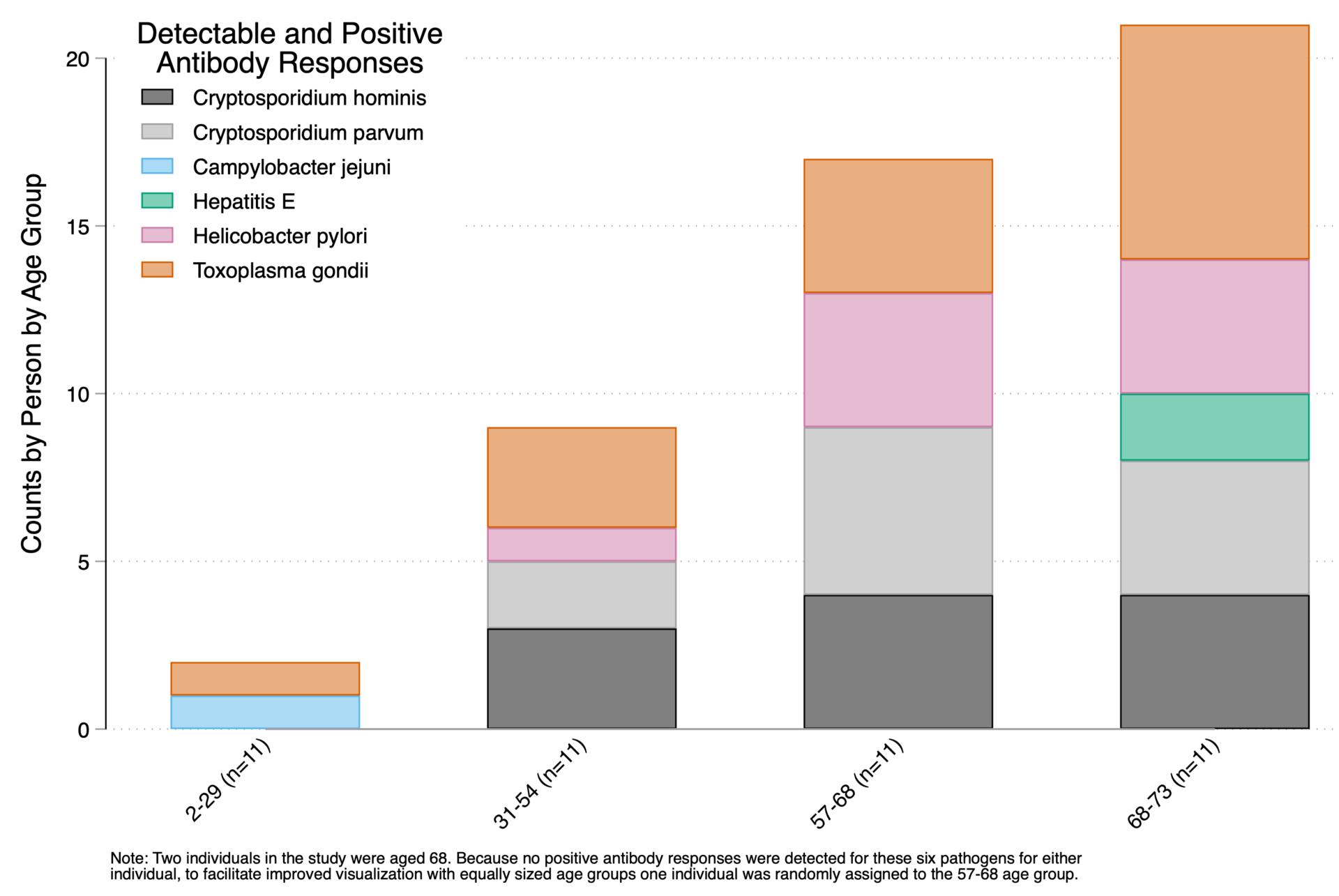
Drinking water sources, quality, and associated health outcomes in Appalachian Virginia: A risk characterization study in two counties
Authors: Cohen*, Rasheduzzaman, O’Connell, Brown, Taniuchi, Krometis, Hubbard, Scheuerman, Edwards, Darling, Pennala, Price, Lytton, Wettstone, Pholwat, Ward, Hallinger, Simmons, Griffin, Kobylanski, Egorov, & Wade
Publication Year: 2024 | Journal / Publisher: International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health
Abstract/Summary: In the US, violations of drinking water regulations are highest in lower-income rural areas overall, and particularly in Central Appalachia. However, data on drinking water use, quality, and associated health outcomes in rural Appalachia are limited. We sought to assess public and private drinking water sources and associated risk factors for waterborne pathogen exposures for individuals living in rural regions of Appalachian Virginia. We administered surveys and collected tap water, bottled water, and saliva samples in lower-income households in two adjacent rural counties in southwest Virginia (bordering Kentucky and Tennessee). Water samples were tested for pH, temperature, conductivity, total coliforms, E. coli, free chlorine, nitrate, fluoride, heavy metals, and specific pathogen targets. Saliva samples were analyzed for antibody responses to potentially waterborne infections. We also shared water analysis results with households. We enrolled 33 households (83 individuals), 82% (n = 27) with utility-supplied water and 18% with private wells (n = 3) or springs (n = 3). 58% (n = 19) reported household incomes of <$20,000/year. Total coliforms were detected in water samples from 33% (n = 11) of homes, E. coli in 12%, all with wells or springs (n = 4), and Aeromonas, Campylobacter, and Enterobacter in 9%, all spring water (n = 3). Diarrhea was reported for 10% of individuals (n = 8), but was not associated with E. coli detection. 34% (n = 15) of saliva samples had detectable antibody responses for Cryptosporidium spp., C. jejuni, and Hepatitis E. After controlling for covariates and clustering, individuals in households with septic systems and straight pipes had significantly higher likelihoods of antibody detection (risk ratios = 3.28, 95%CI = 1.01–10.65). To our knowledge, this is the first study to collect and analyze drinking water samples, saliva samples, and reported health outcome data from low-income households in Central Appalachia. Our findings indicate that utility-supplied water in this region was generally safe, and individuals in low-income households without utility-supplied water or sewerage have higher exposures to waterborne pathogens.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
Perceptions of poverty: Evaluating Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool derived rankings and global development indicators in five African nations
Authors: Minjauw, F., Rasheduzzaman, M., Baumgartner, P., Doward, P., Clarkson, G., & Cohen, A.*
Publication Year: 2024 | Journal / Publisher: Journal of International Development
Abstract/Summary: This study assessed an array of indicators for rural poverty assessments and evaluated use of the Multidimensional Poverty Assessment Tool (MPAT) as a proxy for commonly used indicators, such as the Human Development Index, Gross National Income, Global Hunger Index, and the Gender Inequality Index. MPAT data from 5322 rural households across five countries in Africa were analyzed. While MPAT aligned well with development indicators for Kenya, Lesotho, and Tanzania, this was not the case for Eswatini and Zimbabwe. Overall, MPAT-based rankings correlated well with hunger, food security, and gender equality indicators. Our findings highlight the use of MPAT-derived indices as valuable supplements for commonly used development indicators.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
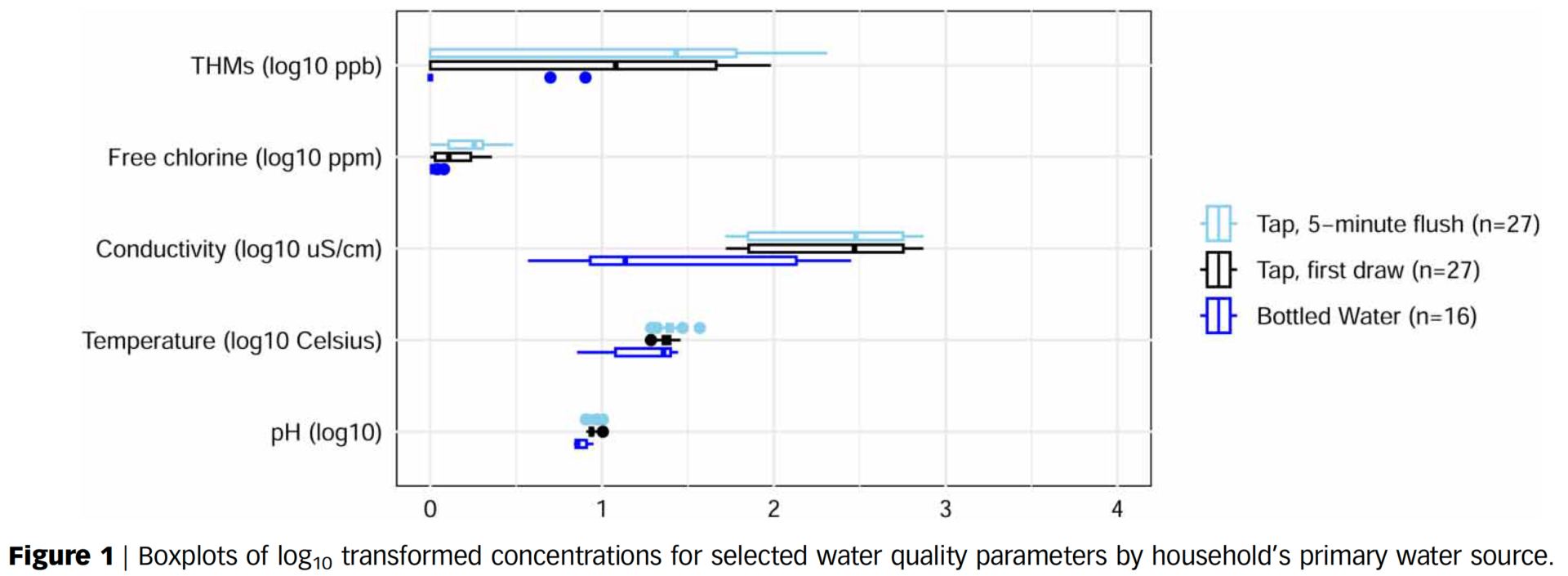
Point-of-use chlorine residuals and disinfection byproduct occurrences in rural households served by public water utilities in Appalachian Virginia
Authors: Rasheduzzaman, M, O’Connell, B., Krometis, L.-A., Brown, T., & Cohen, A.*
Publication Year: 2024 | Journal / Publisher: Journal of Water and Health
Abstract/Summary: We characterized concentrations of trihalomethanes (THMs), a measure of disinfection byproducts (DBPs), in tap water samples collected from households with utility-supplied water in two rural counties in Appalachian Virginia, and assessed associations with pH, free chlorine, and metal ions which can impact THM formation. Free chlorine concentrations in all samples (n = 27 homes) complied with EPA drinking water guidelines, though 7% (n = 2) of first draw samples and 11% (n = 3) of 5-min flushed-tap water samples exceeded the US Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) maximum contaminant level (MCL) for THM (80 ppb). Regression analyses showed that free chlorine and pH were positively associated with the formation of THM levels above SDWA MCLs (OR = 1.04, p = 0.97 and OR = 1.74, p = 0.79, respectively), while temperature was negatively associated (OR = 0.78, p = 0.38). Of the eight utilities serving study households, samples from water served by three different utilities exceeded the EPA MCL for THM. Overall, these findings do not indicate substantial exposures to DBPs for rural households with utility-supplied water in this region of southwest Virginia. However, given the observed variability in THM concentrations between and across utilities, and established adverse health impacts associated with chronic and acute DBP exposure, more research on DBPs in rural Central Appalachia is warranted.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
Bottled and Well Water Quality in a Small Central Appalachian Community: Household-Level Analysis of Enteric Pathogens, Inorganic Chemicals, and Health Outcomes in Rural Southwest Virginia
Authors: Cohen, A., Rasheduzzaman, M., Darling, A., Krometis, L.-A., Edwards, M., Brown, T., Ahmed, T., Wettstone, E., Pholwat, S., Taniuchi, M., & Rogawski McQuade, E. T.
Publication Year: 2022 | Journal / Publisher: International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health
Abstract/Summary: Consumption of unsafe drinking water is associated with a substantial burden of disease globally. In the US, ~1.8 million people in rural areas lack reliable access to safe drinking water. Our objective was to characterize and assess household-level water sources, water quality, and associated health outcomes in Central Appalachia. We collected survey data and water samples (tap, source, and bottled water) from consenting households in a small rural community without utility-supplied water in southwest Virginia. Water samples were analyzed for physicochemical parameters, total coliforms, E. coli, nitrate, sulfate, metals (e.g., arsenic, cadmium, lead), and 30+ enteric pathogens. Among the 69% (n = 9) of households that participated, all had piped well water, though 67% (n = 6) used bottled water as their primary drinking water source. Total coliforms were detected in water samples from 44.4% (n = 4) of homes, E. coli in one home, and enteric pathogens (Aeromonas, Campylobacter, Enterobacter) in 33% (n = 3) of homes. Tap water samples from 11% (n = 1) of homes exceeded the EPA MCL for nitrate, and 33% (n = 3) exceeded the EPA SMCL for iron. Among the 19 individuals residing in study households, reported diarrhea was 25% more likely in homes with measured E. coli and/or specific pathogens (risk ratio = 1.25, cluster-robust standard error = 1.64, p = 0.865). Although our sample size was small, our findings suggest that a considerable number of lower-income residents without utility-supplied water in rural areas of southwest Virginia may be exposed to microbiological and/or chemical contaminants in their water, and many, if not most, rely on bottled water as their primary source of drinking water.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
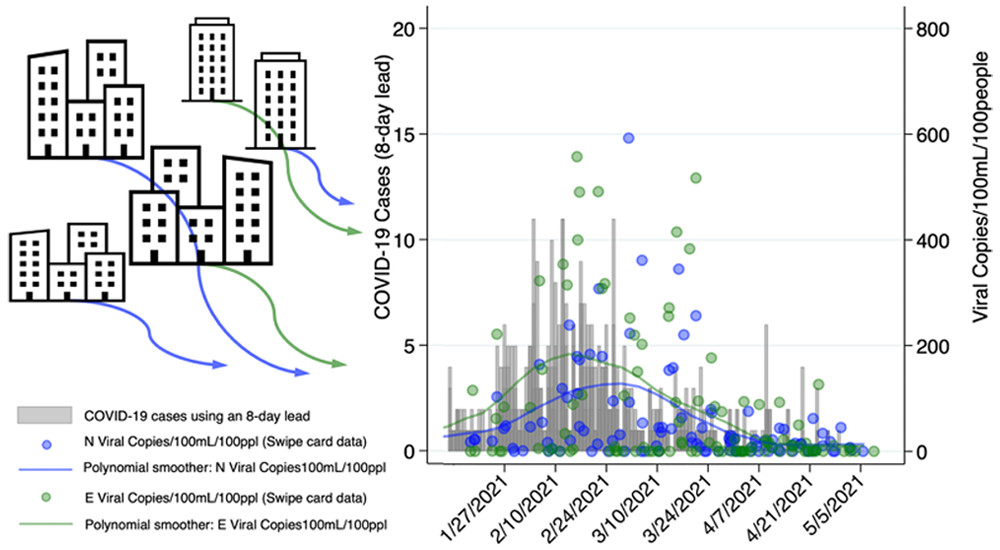
Subsewershed SARS-CoV-2 Wastewater Surveillance & COVID-19 Epidemiology Using Building-specific Occupancy & Case Data
Authors: Cohen, A.,Maile-Moskowitz, A., Grubb, C., Gonzalez, R. A., Ceci, A., Darling, A., Hungerford, L., Fricker, R. D., Finkielstein, C. V., Pruden, A., & Vikesland, P. J.
Publication Year: 2022 | Journal / Publisher: Environmental Science & Technology - Water
Abstract/Summary: To evaluate the use of wastewater-based surveillance and epidemiology to monitor and predict SARS-CoV-2 virus trends, over the 2020–2021 academic year we collected wastewater samples twice weekly from 17 manholes across Virginia Tech’s main campus. We used data from external door swipe card readers and student isolation/quarantine status to estimate building-specific occupancy and COVID-19 case counts at a daily resolution. After analyzing 673 wastewater samples using reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), we reanalyzed 329 samples from isolation and nonisolation dormitories and the campus sewage outflow using reverse transcription digital droplet polymerase chain reaction (RT-ddPCR). Population-adjusted viral copy means from isolation dormitory wastewater were 48% and 66% higher than unadjusted viral copy means for N and E genes (1846/100 mL to 2733/100 mL/100 people and 2312/100 mL to 3828/100 mL/100 people, respectively; n = 46). Prespecified analyses with random-effects Poisson regression and dormitory/cluster-robust standard errors showed that the detection of N and E genes were associated with increases of 85% and 99% in the likelihood of COVID-19 cases 8 days later (incident–rate ratio (IRR) = 1.845, p = 0.013 and IRR = 1.994, p = 0.007, respectively; n = 215), and one-log increases in swipe card normalized viral copies (copies/100 mL/100 people) for N and E were associated with increases of 21% and 27% in the likelihood of observing COVID-19 cases 8 days following sample collection (IRR = 1.206, p < 0.001, n = 211 for N; IRR = 1.265, p < 0.001, n = 211 for E). One-log increases in swipe normalized copies were also associated with 40% and 43% increases in the likelihood of observing COVID-19 cases 5 days after sample collection (IRR = 1.403, p = 0.002, n = 212 for N; IRR = 1.426, p < 0.001, n = 212 for E). Our findings highlight the use of building-specific occupancy data and add to the evidence for the potential of wastewater-based epidemiology to predict COVID-19 trends at subsewershed scales.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
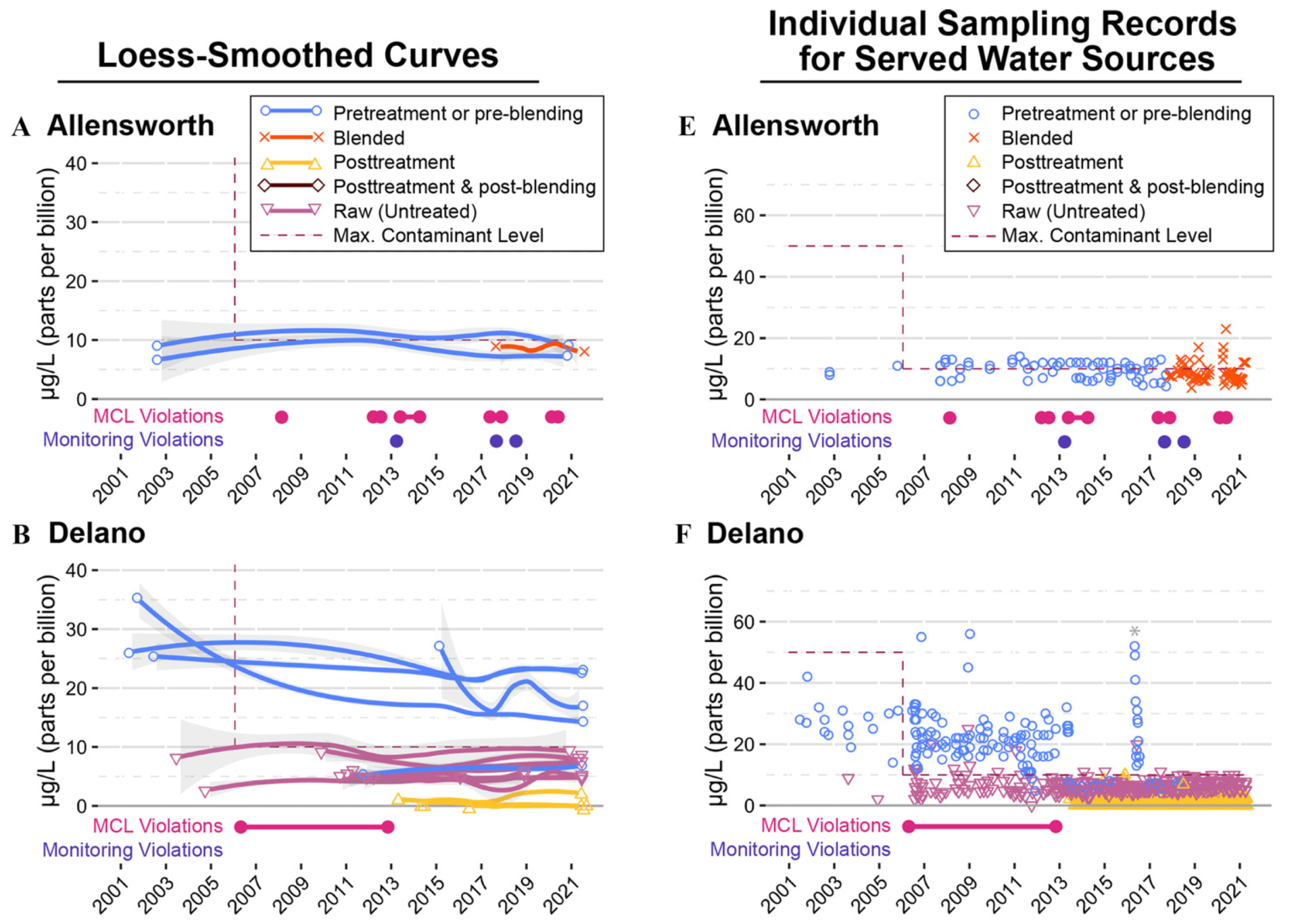
The Human Right to Water: A 20-Year Comparative Analysis of Arsenic in Rural and Carceral Drinking Water Systems in California
Authors: Rempel, J., Ray, I., Hessl, E., Vazin, J., Zhou, Z., Kim, S., Zhang, X., Ding, C., He, Z., Pellow, D., & Cohen, A.
Publication Year: 2022 | Journal / Publisher: Environmental Health Perspectives
Abstract/Summary: Access to safe drinking water is considered a universal human right. In the U.S., exposure to arsenic contamination in drinking water disproportionately impacts small, groundwater-reliant communities and communities of color. Limited research exists on water quality in prisons; however, prisons in the Southwestern U.S. have elevated arsenic concentrations compared to other community water systems (CWS) in the region. In this paper we present a comparative analysis of 20 years of data (2001-2021) on arsenic concentrations in the CWSs serving Kern Valley State Prison (KVSP) and three neighboring rural communities: Allensworth, Delano, and McFarland. Our objective was to better understand trends in water quality, compliance, and treatment following adoption of the revised arsenic MCL, and to elucidate differences, if any, between neighboring incarcerated and non-incarcerated populations.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
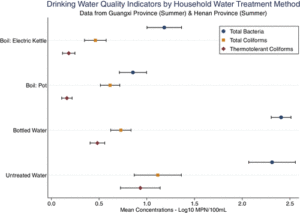
Boiled or Bottled: Regional and Seasonal Exposures to Drinking Water Contamination and Household Air Pollution in Rural China
Authors: Cohen, A., Pillarisetti, A., Luo, Q., Zhang, Q., Li, H., Zhong, G., Zhu, G., Colford, J. M., Smith, K. R., Ray, I., & Tao, Y.
Publication Year: 2020 | Journal / Publisher: Environmental Health Perspectives
Abstract/Summary: We assessed the regional and seasonal prevalence of HWT practices (including bottled water use) in low-income rural areas in two Chinese provinces, evaluated the microbiological safety of drinking water and associated health outcomes, and estimated the air pollution burden associated with the use of solid fuels for boiling. Methods: We conducted cross-sectional surveys and collected drinking water samples from 1,033 rural households in Guangxi and Henan provinces. Temperature sensors affixed to pots and electric kettles were used to corroborate self-reported boiling frequencies and durations, which were used to model household air pollution (HAP) in terms of estimated particulate matter ≤2.5μm in aerodynamic diameter (PM2.5) concentrations. Results: Based on summer data collection in both provinces, after controlling for covariates, boiling with electric kettles was associated with the largest log reduction in thermotolerant coliforms (TTCs) (0.66log10 TTC most probable number/100mL), followed by boiling with pots (−0.58), and bottled water use (−0.39); all were statistically significant (p<0.001). Boiling with electric kettles was associated with a reduced risk of TTC contamination [risk ratio (RR)=0.25, p<0.001] and reported diarrhea (RR=0.80, p=0.672). TTCs were detected in 51% (n=136) of bottled water samples. For households boiling with biomass, modeled PM2.5 concentrations averaged 79 μg/m3 (standard deviation=21). Discussion: Our findings suggest that where boiling is already common and electricity access is widespread, the promotion of electricity-based boiling may represent a pragmatic stop-gap means of expanding safe water access until centralized, or decentralized, treated drinking water is available; displacing biomass use for water boiling could also reduce HAP concentrations and exposures. Our results also highlight the risks of increasing bottled water use in rural areas, and its potential to displace other sources of safe drinking water, which could in turn hamper efforts in China and other LMICs toward universal and affordable safe water access.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
Intermittent water supply management, household adaptation, & drinking water quality: A comparative study in two Chinese provinces
Authors: Li, H., Cohen, A., Li, Z., Lu, S., He, Z., Wang, L., & Zhang, X.
Publication Year: 2020 | Journal / Publisher: Water
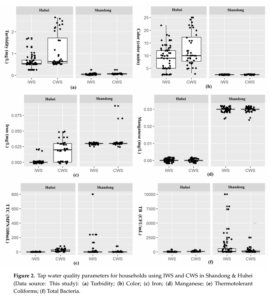 Abstract/Summary: Intermittent water supply (IWS) is a relatively common phenomenon across the world as well as in rural and peri-urban areas across China, though there has been little IWS-focused research from China published to date. IWS consumers typically adopt a range of strategies to cope with insufficient water supply, poor drinking water quality, and associated inconveniences. In this study, we collected a range of data from small-scale utilities and households in two IWS systems and two continuous water supply (CWS) systems, as well as from comparison groups, in Shandong and Hubei provinces. Data collection included water quality testing, interviews, and surveys on behavioral adaptations, coping strategies, water-related health perceptions, and other metrics of consumer satisfaction. Overall, we found that the IWS coping strategies employed in northern China (Shandong) were associated with generally safe, but inconvenient, water access, whereas adaptation strategies observed in southern China (Hubei) appeared to improve convenience, but not water quality. Compared to the CWS comparison groups, we did not observe significant differences in waterand sanitation-related behaviors in the IWS groups, suggesting interventions to increase adaptive and protective behaviors at the household level might further improve safe water access for households living with IWS. Overall, although the water supply infrastructure in these study areas appeared to be in relatively good condition, in contrast to reported data on IWS systems in other countries, we observed multiple risk factors associated with the water treatment and distribution processes in these IWS systems. Among policy recommendations, our results suggest that the implementation of Water Safety Plans in China would likely improve the management of drinking water treatment and, by extension, safe drinking water supply under conditions of IWS.
Abstract/Summary: Intermittent water supply (IWS) is a relatively common phenomenon across the world as well as in rural and peri-urban areas across China, though there has been little IWS-focused research from China published to date. IWS consumers typically adopt a range of strategies to cope with insufficient water supply, poor drinking water quality, and associated inconveniences. In this study, we collected a range of data from small-scale utilities and households in two IWS systems and two continuous water supply (CWS) systems, as well as from comparison groups, in Shandong and Hubei provinces. Data collection included water quality testing, interviews, and surveys on behavioral adaptations, coping strategies, water-related health perceptions, and other metrics of consumer satisfaction. Overall, we found that the IWS coping strategies employed in northern China (Shandong) were associated with generally safe, but inconvenient, water access, whereas adaptation strategies observed in southern China (Hubei) appeared to improve convenience, but not water quality. Compared to the CWS comparison groups, we did not observe significant differences in waterand sanitation-related behaviors in the IWS groups, suggesting interventions to increase adaptive and protective behaviors at the household level might further improve safe water access for households living with IWS. Overall, although the water supply infrastructure in these study areas appeared to be in relatively good condition, in contrast to reported data on IWS systems in other countries, we observed multiple risk factors associated with the water treatment and distribution processes in these IWS systems. Among policy recommendations, our results suggest that the implementation of Water Safety Plans in China would likely improve the management of drinking water treatment and, by extension, safe drinking water supply under conditions of IWS.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
Fuel use trends for boiling water in rural China (1992-2012) & environmental health implications: A national cross-sectional study
Authors: Du, W., Cohen, A., Shen, G., Ru, M., Shen, H., & Shu, T.
Publication Year: 2018 | Journal / Publisher: Environmental Science & Technology
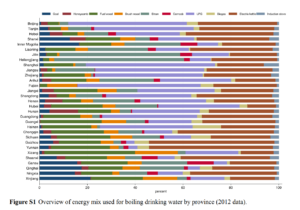 Abstract/Summary:Survey data from a comprehensive national survey of ∼34 000 households were analyzed for the mix status and transition trajectory of energy for boiling water in rural Chinese households from 1992 to 2012. In 1992, ∼6% of households reported using electricity, biogas, or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) to boil drinking water; in 2012, the proportion was ∼60%. Income per capita appeared most strongly associated with this transition toward electricity and other clean fuels. Median annual incomes for households using biomass fuels, electric kettles, and LPG were RMB 15 000, 28 000, and 30 000, respectively. Overall, the transition was most pronounced in eastern China, a region which experienced relatively higher rates of economic growth over the same 20-year period. Energy type preferences appear to be highly dependent on fuel accessibility such that coal and straw usage was higher in provinces with higher coal and grain production. These trends suggest that electric kettle use would likely increase from ∼29% (2012) to ∼60% by 2030, at which point <5% of rural households would be expected to boil with solid fuels. Recent evidence suggests that this transition could contribute to reductions in water-related gastrointestinal illness as well as reductions in air pollutant emissions in rural China.
Abstract/Summary:Survey data from a comprehensive national survey of ∼34 000 households were analyzed for the mix status and transition trajectory of energy for boiling water in rural Chinese households from 1992 to 2012. In 1992, ∼6% of households reported using electricity, biogas, or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) to boil drinking water; in 2012, the proportion was ∼60%. Income per capita appeared most strongly associated with this transition toward electricity and other clean fuels. Median annual incomes for households using biomass fuels, electric kettles, and LPG were RMB 15 000, 28 000, and 30 000, respectively. Overall, the transition was most pronounced in eastern China, a region which experienced relatively higher rates of economic growth over the same 20-year period. Energy type preferences appear to be highly dependent on fuel accessibility such that coal and straw usage was higher in provinces with higher coal and grain production. These trends suggest that electric kettle use would likely increase from ∼29% (2012) to ∼60% by 2030, at which point <5% of rural households would be expected to boil with solid fuels. Recent evidence suggests that this transition could contribute to reductions in water-related gastrointestinal illness as well as reductions in air pollutant emissions in rural China.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
Predictors of drinking water boiling & bottled water consumption in rural China: A hierarchical modeling approach
Authors: Cohen, A., Zhang, Q., Luo, Q., Tao, Y., Colford, J. M., & Ray, I.
Publication Year: 2017 | Journal / Publisher: Environmental Science & Technology
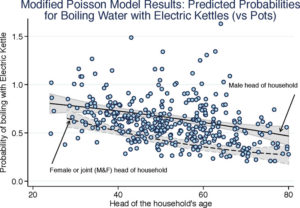 Abstract/Summary: Approximately two billion people drink unsafe water. Boiling is the most commonly used household water treatment (HWT) method globally and in China. HWT can make water safer, but sustained adoption is rare and bottled water consumption is growing. To successfully promote HWT, an understanding of associated socioeconomic factors is critical. We collected survey data and water samples from 450 rural households in Guangxi Province, China. Covariates were grouped into blocks to hierarchically construct modified Poisson models and estimate risk ratios (RR) associated with boiling methods, bottled water, and untreated water. Female-headed households were most likely to boil (RR = 1.36, p < 0.01), and among boilers those using electric kettles rather than pots had higher income proxies (e.g., per capita TV ownership RR = 1.42, p < 0.01). Higher-income households with younger, literate, and male heads were more likely to purchase (frequently contaminated) bottled water, or use electric kettles if they boiled. Our findings show that boiling is not an undifferentiated practice, but one with different methods of varying effectiveness, environmental impact, and adoption across socioeconomic strata. Our results can inform programs to promote safer and more efficient boiling using electric kettles, and suggest that if rural China’s economy continues to grow then bottled water use will increase.
Abstract/Summary: Approximately two billion people drink unsafe water. Boiling is the most commonly used household water treatment (HWT) method globally and in China. HWT can make water safer, but sustained adoption is rare and bottled water consumption is growing. To successfully promote HWT, an understanding of associated socioeconomic factors is critical. We collected survey data and water samples from 450 rural households in Guangxi Province, China. Covariates were grouped into blocks to hierarchically construct modified Poisson models and estimate risk ratios (RR) associated with boiling methods, bottled water, and untreated water. Female-headed households were most likely to boil (RR = 1.36, p < 0.01), and among boilers those using electric kettles rather than pots had higher income proxies (e.g., per capita TV ownership RR = 1.42, p < 0.01). Higher-income households with younger, literate, and male heads were more likely to purchase (frequently contaminated) bottled water, or use electric kettles if they boiled. Our findings show that boiling is not an undifferentiated practice, but one with different methods of varying effectiveness, environmental impact, and adoption across socioeconomic strata. Our results can inform programs to promote safer and more efficient boiling using electric kettles, and suggest that if rural China’s economy continues to grow then bottled water use will increase.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF
Microbiological evaluation of household drinking water treatment in rural China shows benefits of electric kettles: A cross-sectional study
Authors: Cohen, A., Tao, Y., Luo, Q., Zhong, G., Romm, J., Colford, J. M., & Ray, I.
Publication Year: 2015 | Journal / Publisher: PLoS ONE
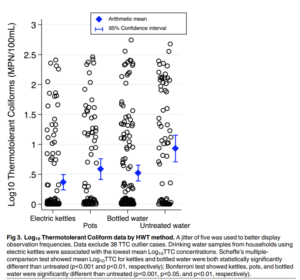 Abstract: Background – In rural China ~607 million people drink boiled water, yet little is known about prevailing household water treatment (HWT) methods or their effectiveness. Boiling, the most common HWT method globally, is microbiologically effective, but household air pollution (HAP) from burning solid fuels causes cardiovascular and respiratory disease, and black carbon emissions exacerbate climate change. Boiled water is also easily re-contaminated. Our study was designed to identify the HWT methods used in rural China and to evaluate their effectiveness. Methods – We used a geographically stratified cross-sectional design in rural Guangxi Province to collect survey data from 450 households in the summer of 2013. Household drinking water samples were collected and assayed for Thermotolerant Coliforms (TTC), and physicochemical analyses were conducted for village drinking water sources. In the winter of 2013–2104, we surveyed 120 additional households and used remote sensors to corroborate selfreported boiling data. Findings – Our HWT prevalence estimates were: 27.1% boiling with electric kettles, 20.3% boiling with pots, 34.4% purchasing bottled water, and 18.2% drinking untreated water (for these analyses we treated bottled water as a HWT method). Households using electric kettles had the lowest concentrations of TTC (73% lower than households drinking untreated water). Multilevel mixed-effects regression analyses showed that electric kettles were associated with the largest Log10TTC reduction (-0.60, p<0.001), followed by bottled water (-0.45, p<0.001) and pots (-0.44, p<0.01). Compared to households drinking untreated water, electric kettle users also had the lowest risk of having TTC detected in their drinking water (risk ratio, RR = 0.49, 0.34–0.70, p<0.001), followed by bottled water users (RR = 0.70, 0.53–0.93, p<0.05) and households boiling with pots (RR = 0.74, 0.54–1.02, p = 0.06). Conclusion: As far as we are aware, this is the first HWT-focused study in China, and the first to quantify the comparative advantage of boiling with electric kettles over pots. Our results suggest that electric kettles could be used to rapidly expand safe drinking water access and reduce HAP exposure in rural China.
Abstract: Background – In rural China ~607 million people drink boiled water, yet little is known about prevailing household water treatment (HWT) methods or their effectiveness. Boiling, the most common HWT method globally, is microbiologically effective, but household air pollution (HAP) from burning solid fuels causes cardiovascular and respiratory disease, and black carbon emissions exacerbate climate change. Boiled water is also easily re-contaminated. Our study was designed to identify the HWT methods used in rural China and to evaluate their effectiveness. Methods – We used a geographically stratified cross-sectional design in rural Guangxi Province to collect survey data from 450 households in the summer of 2013. Household drinking water samples were collected and assayed for Thermotolerant Coliforms (TTC), and physicochemical analyses were conducted for village drinking water sources. In the winter of 2013–2104, we surveyed 120 additional households and used remote sensors to corroborate selfreported boiling data. Findings – Our HWT prevalence estimates were: 27.1% boiling with electric kettles, 20.3% boiling with pots, 34.4% purchasing bottled water, and 18.2% drinking untreated water (for these analyses we treated bottled water as a HWT method). Households using electric kettles had the lowest concentrations of TTC (73% lower than households drinking untreated water). Multilevel mixed-effects regression analyses showed that electric kettles were associated with the largest Log10TTC reduction (-0.60, p<0.001), followed by bottled water (-0.45, p<0.001) and pots (-0.44, p<0.01). Compared to households drinking untreated water, electric kettle users also had the lowest risk of having TTC detected in their drinking water (risk ratio, RR = 0.49, 0.34–0.70, p<0.001), followed by bottled water users (RR = 0.70, 0.53–0.93, p<0.05) and households boiling with pots (RR = 0.74, 0.54–1.02, p = 0.06). Conclusion: As far as we are aware, this is the first HWT-focused study in China, and the first to quantify the comparative advantage of boiling with electric kettles over pots. Our results suggest that electric kettles could be used to rapidly expand safe drinking water access and reduce HAP exposure in rural China.
PDF on Publisher Website | PDF on OSF